The Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI) are two technologies that have been rapidly advancing in recent years. IoT refers to the interconnectivity of devices and sensors that can collect and exchange data, while AI involves the development of algorithms and software that can perform intelligent tasks. These technologies are becoming increasingly integrated, with AI being used to process and analyze the vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices.
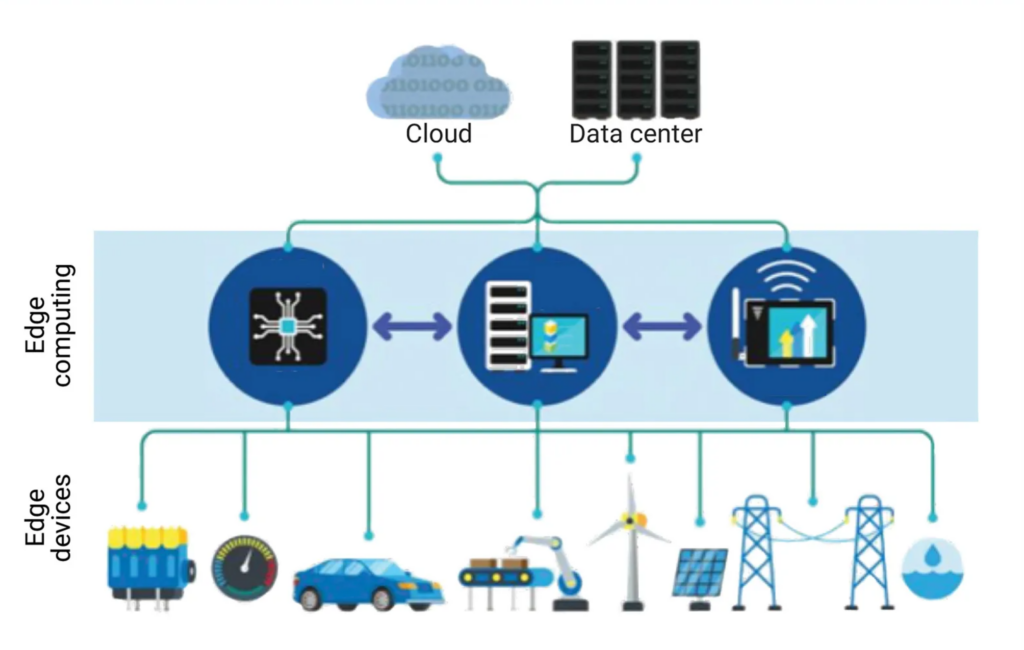
One area that is particularly important for both IoT and AI is edge computing. This refers to the practice of processing and analyzing data closer to the source, rather than sending it all to a centralized cloud for analysis. This approach can significantly reduce latency and improve the overall efficiency of the system.

The Impact of Edge Computing on IoT and AI
Edge computing has had a significant impact on both IoT and AI. By enabling data processing and analysis closer to the source, edge computing has reduced the amount of data that needs to be sent to the cloud for analysis. This can significantly reduce latency, improve system performance, and enable real-time decision-making.
There are several benefits to using edge computing for IoT applications. One of the most significant is improved performance, as edge computing can enable real-time data processing and analysis. This can be particularly important for applications that require fast response times, such as autonomous vehicles or industrial control systems.
Examples of edge devices in IoT include the Raspberry Pi 4B+ and the Nvidia Nano. These devices are small and powerful, making them ideal for use in edge computing applications. Other popular devices include the Nvidia Jetson Nano and Nvidia Orion, as well as Arduino-based platforms.
The Role of Edge Computing in IoT
Edge computing plays a critical role in IoT by enabling data processing and analysis to occur closer to the source, reducing latency and improving the overall efficiency of the system. This is particularly important for applications that require fast response times or real-time decision-making.
One key difference between edge computing and IoT is that edge computing refers specifically to the practice of processing and analyzing data closer to the source. The edge layer of IoT refers to the layer of devices and sensors that collect data and transmit it to the cloud for analysis.
There are two roles played by edge IT in IoT systems. The first is data processing and analysis, which is performed at the edge to reduce latency and improve system performance. The second is data aggregation, which involves collecting data from multiple edge devices and transmitting it to the cloud for further analysis.
Types of Edge Computing
There are three main types of edge computing: on-premise edge computing, cloud-based edge computing, and hybrid edge computing.
On-premise edge computing refers to the deployment of edge devices within a local network, allowing for data processing and analysis to occur closer to the source.
Cloud-based edge computing involves using cloud infrastructure to deploy and manage edge devices, allowing for increased scalability and flexibility.
Hybrid edge computing combines both on-premise and cloud-based edge computing to leverage the benefits of both approaches.
Edge AI Devices
Edge AI devices, such as the Nvidia Jetson Nano and the Raspberry Pi 4B+, are specialized devices designed for running AI algorithms at the edge of the network. These devices offer powerful computing capabilities while also being low-cost and energy-efficient.
Use Cases of Edge Computing in IoT and AI
Edge computing has numerous use cases in IoT and AI, including:
- Smart homes and buildings: edge devices can be used to collect data from various sensors and devices within a building, enabling the automation of tasks such as lighting and temperature control.
- Smart cities: edge devices can be used to collect data on traffic flow, air quality, and other environmental factors, allowing for the optimization of city infrastructure and services.
- Industrial IoT: edge computing can be used to optimize manufacturing processes, reducing downtime and improving efficiency.
- Healthcare: edge devices can be used to collect data from medical devices, enabling real-time monitoring and analysis of patient health.
Edge computing is revolutionizing the way IoT and AI applications are developed and deployed. By enabling data processing and analysis to occur closer to the source, edge computing offers numerous benefits such as reduced latency, improved efficiency, and increased scalability. With the emergence of low-cost and energy-efficient edge devices, the possibilities for edge computing in IoT and AI are endless.
Flo Mobility has been working Edge compute devices for a while and have developed one of its own Flo Edge one. It is Edge compute unit that comes with onboard integrated sensors and has out of the box AI capabilities.


